Atmospheric pressure, the pervasive yet often imperceptible force exerted by the column of air above us, plays a pivotal role in countless natural phenomena and technological advancements. This omnipresent weight, a fundamental property of our planet’s atmosphere, influences everything from weather patterns to the very efficacy of delicate medical instruments. Its subtle fluctuations hold a wealth of information, waiting to be deciphered.
Enter the silent workhorse: atmospheric pressure sensors. These ingenious transducers convert physical pressure into measurable electrical signals, effectively granting us a window into this unseen world. Far from mere curiosities, these devices are the linchpin of myriad systems, quietly enabling precision, safety, and innovation across a vast spectrum of industries. Their utility, often overlooked, is truly foundational.
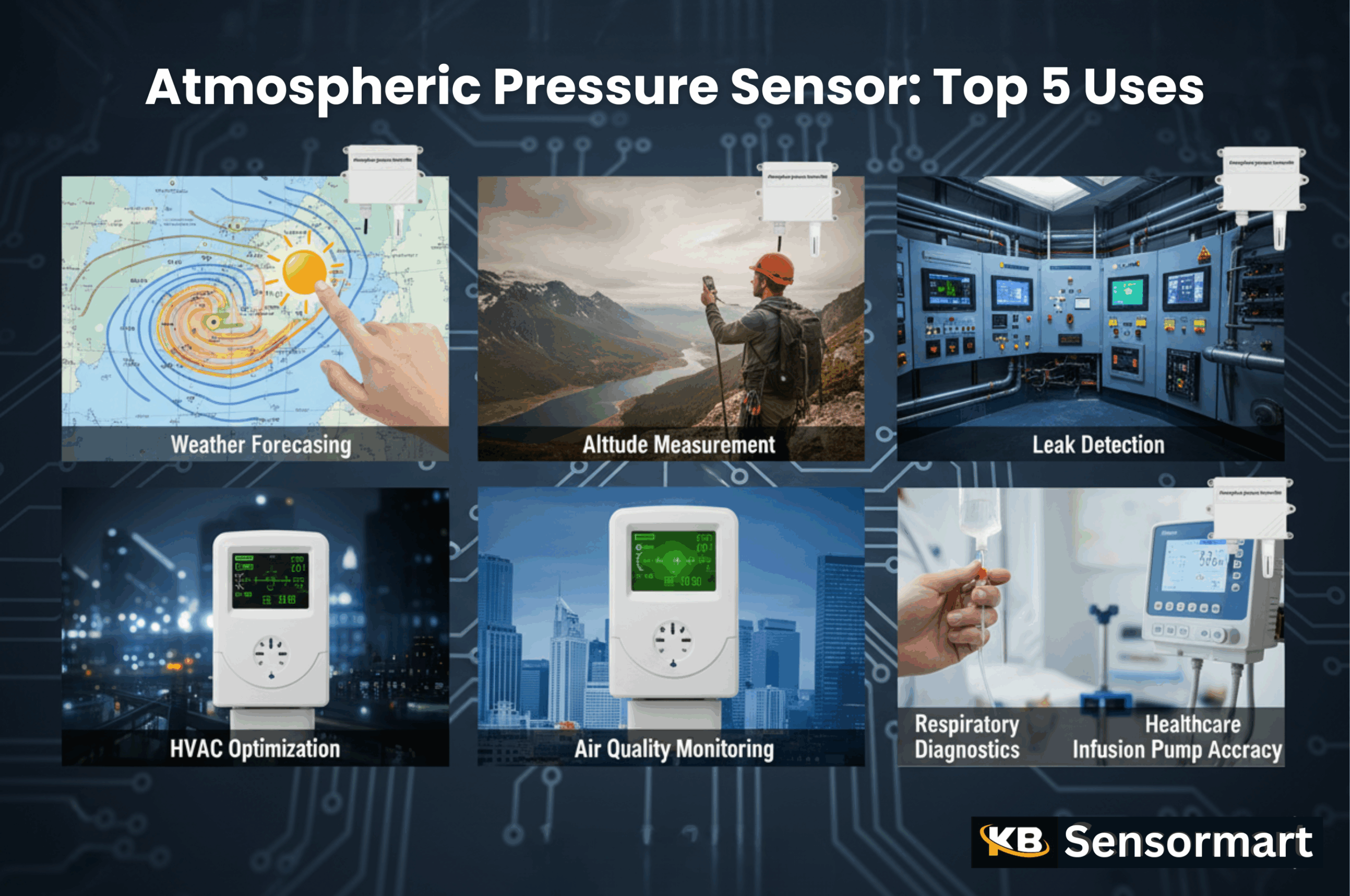
Meteorological Marvels: Weather Forecasting
One of the most widely recognized applications of atmospheric pressure sensors lies within the domain of meteorology, specifically in barometric altimetry and weather prediction. A decrement in atmospheric pressure frequently presages inclement weather, such as an impending storm, while an ascent often signals stable, fair conditions. Weather stations worldwide rely on these sensors to gather real-time data, which is then integrated into complex numerical weather prediction models. These models, leveraging historical data and current readings, forecast future atmospheric states with remarkable accuracy.
Moreover, these sensors are instrumental in storm front detection. Rapid drops in barometric pressure are definitive harbingers of severe weather events like hurricanes, tornadoes, and intense thunderstorms. By continuously monitoring these changes, meteorologists can issue timely warnings, allowing communities to prepare and mitigate potential hazards. The precision of these sensors is paramount in safeguarding lives and property from nature’s more formidable expressions.
Navigational Nexus: Altitude Measurement
In the realm of navigation, atmospheric pressure sensors are indispensable, particularly for aeronautical altimeters. Aircraft utilize these sensors to determine their altitude above sea level. As an aircraft ascends, the atmospheric pressure decreases in a predictable manner. The altimeter translates this pressure into an altitude reading, providing pilots with crucial information for safe flight operations, air traffic control, and adherence to flight paths. This reliance on pressure is a fundamental tenet of aviation.
Beyond the aerosphere, these sensors contribute to GPS augmentation and terrestrial navigation. While GPS provides horizontal positioning, its accuracy for vertical data can be augmented by a local atmospheric pressure sensor. Devices like smartphones and wearable trackers incorporate these sensors to provide more precise altitude readings, which is invaluable for hikers, mountaineers, and even for navigating multi-story buildings. This synergistic relationship enhances location-based services significantly.
Industrial Ingenuity: Process Control
Within industrial settings, atmospheric pressure sensors are pivotal for HVAC optimization. Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning systems frequently employ these sensors to monitor differential pressures across filters, ducts, and controlled environments. Maintaining optimal pressure levels ensures efficient air circulation, prevents contamination in cleanrooms, and contributes to energy conservation. An unoptimized HVAC system can be an egregious waste of resources, making these sensors critical.
Furthermore, these sensors are vital components in leak detection systems. In sealed environments or critical gas lines, even minute changes in atmospheric pressure can indicate a breach. By continuously monitoring pressure, these sensors can quickly pinpoint leaks, preventing material losses, safeguarding personnel from hazardous substances, and ensuring the integrity of industrial processes. This prophylactic application is a testament to their critical utility.
Environmental Stewardship: Air Quality Monitoring
In the pressing pursuit of environmental health, atmospheric pressure sensors are integral to air quality monitoring. They aid in particulate dispersion modeling by providing essential data on atmospheric stability. Pressure readings help determine how pollutants, such as fine particulate matter (PM2.5) or industrial emissions, will disperse or concentrate in the ambient air. This information is crucial for understanding pollution trajectories and their potential impact on public health.
Moreover, these sensors contribute to early warning systems for pollution events. Abrupt changes in local atmospheric pressure, often coupled with other meteorological data, can signal atmospheric inversions—conditions where a layer of warm air traps cooler air below, exacerbating pollution levels. By detecting these precursors, environmental agencies can issue alerts, prompting measures to mitigate exposure and protect vulnerable populations. This proactive capability is invaluable.
Medical Metrology: Healthcare Applications
The precision afforded by atmospheric pressure sensors has found significant utility in the delicate domain of medical metrology. For instance, in respiratory diagnostics, these sensors are integrated into spirometers and other pulmonary function testing devices. They measure the subtle pressure changes associated with inhalation and exhalation, quantifying lung capacity, airflow rates, and other vital parameters. This data is indispensable for diagnosing respiratory ailments such as asthma, COPD, and sleep apnea.
Additionally, these sensors enhance the accuracy of infusion pumps. In medical settings, precise delivery of fluids and medications is non-negotiable. Pressure sensors within these pumps monitor the fluid flow, ensuring that medications are administered at the correct rate and volume. Any anomaly in pressure can indicate a blockage or a faulty delivery, triggering alarms and preventing potential patient harm. This meticulous control underscores their life-saving potential.
Beyond the Obvious: Emerging Applications
The versatility of atmospheric pressure sensors extends far beyond the obvious and into burgeoning technological frontiers. In smart home integration, these sensors are being incorporated into intelligent systems to enhance comfort and efficiency. They can detect changes in indoor air pressure to optimize ventilation, adjust thermostat settings, or even trigger air purifiers, contributing to a more responsive and energy-efficient living environment.
Furthermore, these sensors are making inroads into sports and fitness tracking. Wearable devices leverage atmospheric pressure data to provide more accurate readings for altitude gain during hiking or climbing. This precise elevational information enhances the user’s understanding of their physical exertion and provides richer data for training regimens and activity analysis. The miniature scale of modern sensors makes such integration seamless.
The Ubiquity of Pressure Sensing
From the tempestuous breath of an approaching storm to the gentle ebb and flow of a human breath, atmospheric pressure sensors are the silent arbiters of essential data. Their ubiquitous integration across disparate fields — meteorology, navigation, industry, environmental science, medicine, and consumer technology — underscores their foundational importance. These unassuming devices, often hidden from view, consistently unravel the secrets of the unseen force, enabling a world of greater precision, safety, and informed decision-making. Their continued evolution promises even more ingenious applications in the years to come.





Leave a Reply