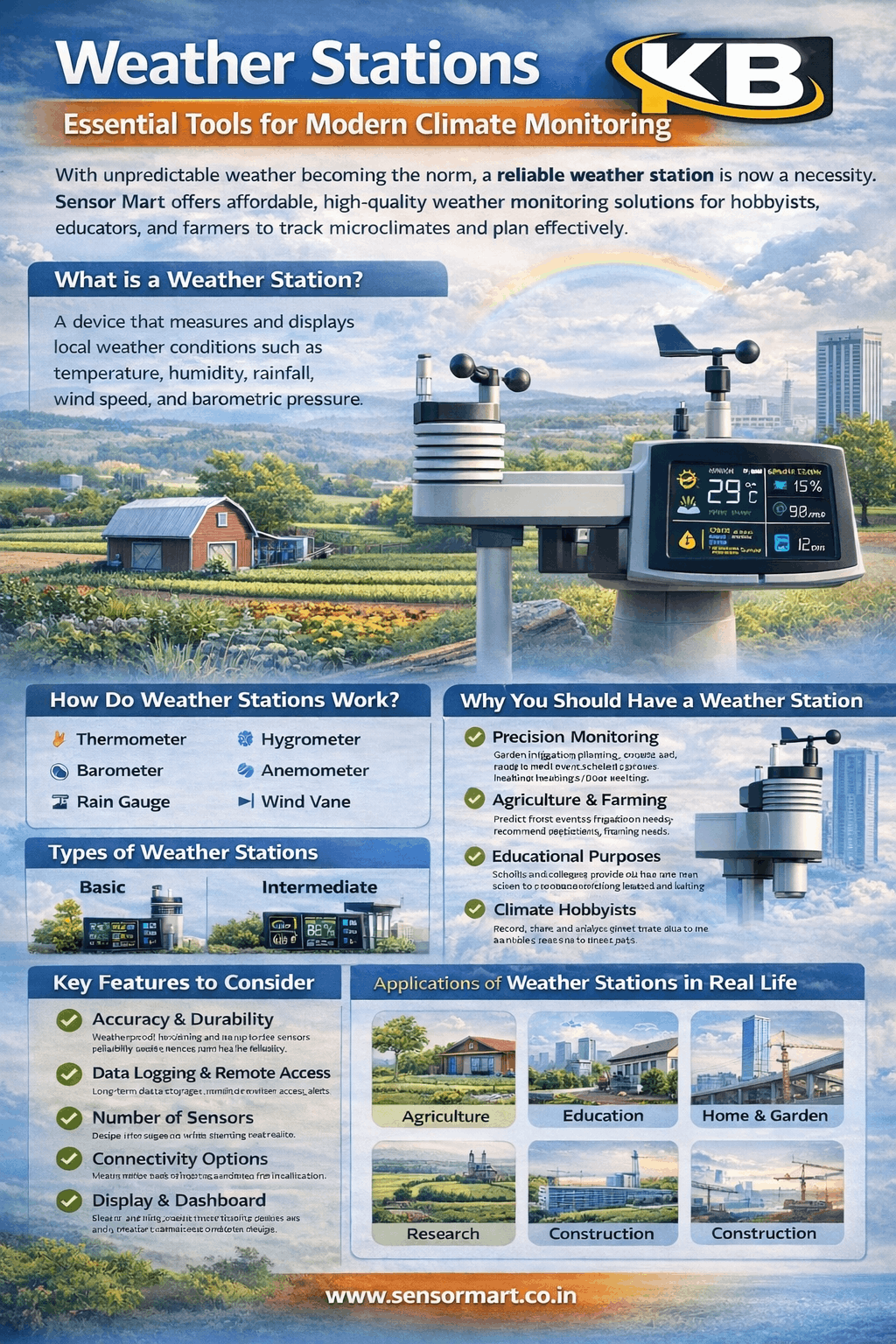
Complete Guide of Moisture Sensor
Complete Guide to Soil Moisture Sensor , Water management, smart agriculture and monitoring the environment are all essential for growing food in our global economy today and for the development of our future. The three devices that lead the charge in these fields include an Electronic Communication (EC) Sensor, a Water Measure Transmitter, and a Soil Moisture Sensor. They are all designed to create an even more productive agricultural environment by conserving water and providing optimal conditions for growing food, including irrigation, hydroponics and all other types of industrial production.
The goal of this guide is to provide information on these three technologies including how they work, where they can be found and why modern systems rely so heavily on them.
The purpose of an EC Sensor
is to measure a solution’s electrical conductivity, which reflects the concentration of various dissolved salts and nutrients that are present in a solution. In agriculture, hydroponics, aquaculture, waste management, and ecologically related monitoring, evaluating a solution’s electrical conductivity is critical for accurate assessment of the solutions’ characteristics.
An electrical conductivity sensor can provide insight into the quality of the water used for plant growth. Additionally, it can be used to assess the level of nutrients in fertilizers, and whether or not a nutrient balance exists between soil moisture and the amount of water being applied. When used in conjunction with a water measure transmitter sensor and a soil moisture sensor, an EC sensor can allow for accurate nutrient application by farmers. Farmers rely on an EC sensor to ensure that they are applying the proper amount of fertilizers to crops.
Some uses for the EC Sensor are irrigation control, greenhouse automation/wastewater management/industrial processing. In all of these cases, monitoring both nutrient and salinity levels would be impossible without an EC sensor.
What’s a Water Measurement Transmitter?
A water measurement transmitter is an instrument that measures the water level, flow rate, pressure, and/or volume and transmits the information it gathers to a control centre. This device is typically used in agricultural applications (eg, irrigation), as well as water storage tanks, reservoirs, pipelines, and wastewater treatment facilities (WWTFs).Complete Guide to EC Sensor
If you pair a water measuring transmitter with an EC sensor and a soil moisture sensor, you have complete water management capabilities — a water measurement transmitter guarantees the proper amount of water will be applied based upon information provided by the soil moisture sensor and any nutrient feedback from the EC sensor.
Water measurement transmitters are essential for monitoring water in real time on modern farms and in smart cities and for analysing water consumption and automating the management of water.
What is Soil Moisture Sensor
The Soil Moisture Sensor is an instrument that measures the amount of moisture contained in the soil. The Soil Moisture Sensor is an essential instrument for the process of precision irrigation. It identifies when a farmer should irrigate his or her crop and how much water they should apply to each acre of land. When combined with the Water Measure Transmitter and EC Sensor through the integration of the Soil Moisture Sensor, irrigation systems will automatically operate without human intervention, providing the highest efficiency of operation. The use of the Soil Moisture Sensor saves water, protects crops from drought conditions, and increases the rate of yield production. The Soil Moisture Sensor has a variety of uses in agricultural production; landscaping; turf management; forest management; and research institutions for scientists working to develop new products or processes.
Combining the EC Sensor, Water Measure Transmitter and Soil Moisture Sensor creates an effective monitoring system.
- The Soil Moisture Sensor measures the amount of moisture in soil.
- The EC Sensor measures the concentration of nutrients in the soil.
- The Water Measure Transmitter measures and controls the amount of water provided to plants.
- The combination of all three sensors creates the core of smart irrigation and environmental monitoring systems.
Farming has developed technologically using the EC Sensor, Water Measure Transmitter, and Soil Moisture Sensors to determine when crops are thirsty; the Water Measure Transmitter accurately applies the right amount of water to the field; the EC Sensor confirms the nutrient balance within the system through the right ratio of electrical conductivity within the soil. Together they save farmers money, conserve water, improve crop yield, and help produce higher-quality crops.
Hydroponics is heavily reliant on the Electrical Conductivity (EC) Sensor
to properly manage and maintain nutrient solutions, while the Water Measure Transmitter is used for monitoring the flow of water in both the circulation and reservoir tanks. Additionally, Soil Moisture Sensors are often used when hybrid systems utilize substrate for plant growth.
The Electrical Conductivity Sensor, Water Measure Transmitter and Soil Moisture Sensor work together to provide a stable environment for all types of plants grown within a controlled environment.
In municipal water and wastewater treatment, Water Measure Transmitters are used to document the flow and storage of treated water, and the Electrical Conductivity Sensors provide constant monitoring of the quality of the treated water, while Soil Moisture Sensors provide support for studies on groundwater and the environment.
Together, the Electrical Conductivity Sensor, Water Measure Transmitter and Soil Moisture Sensors provide real-time data for improved decision making.Complete Guide to Soil Moisture Sensor
Benefits Of Using this Sensor
While the integration of each of three sensors – EC sensor, Water Measure Transmitter and Soil Moisture Sensor – may offer multiple benefits, here are a few examples of how using all three together will help reduce water consumption; enhance overall health of crops; increase yield potential; decrease fertilizer costs; protect our environment.
The integration of all three sensors is the foundation for implementing precision farming practices.
As technology evolves, the future of using an EC sensor, Water Measure Transmitter and Soil Moisture Sensor is going to be increasingly more sophisticated and less expensive through use of AI and IoT platforms. Farm operations and water management systems will be fully automated by utilizing data from these three sensors.
Conclusion
The EC Sensor, Water Measure Transmitter, and Soil Moisture Sensor are no longer optional tools — they are essential components of modern agriculture, water management, and environmental monitoring.
From improving irrigation efficiency to protecting natural resources, the EC Sensor, Water Measure Transmitter, and Soil Moisture Sensor work together to build a smarter, more sustainable future.
If you want higher productivity, lower costs, and responsible resource management, investing in the EC Sensor, Water Measure Transmitter, and Soil Moisture Sensor is the smartest decision you can make.
FAQ
1. What is an EC Sensor?
An EC Sensor (Electrical Conductivity Sensor) is a device used to measure the ability of water or liquid solutions to conduct electricity. This measurement indicates the amount of dissolved salts or nutrients present in the liquid.
2. Why is an EC Sensor important?
An EC Sensor is important because it helps determine water quality and nutrient concentration. It is widely used in agriculture, hydroponics, aquaculture, irrigation, water treatment, and environmental monitoring.
3. How does an EC Sensor work?
An EC Sensor works by applying a small electrical voltage between two electrodes in a liquid and measuring how easily the current flows. Higher conductivity means more dissolved salts or nutrients are present.
4. Where is an EC Sensor used?
An EC Sensor is used in:
- Agriculture and irrigation systems
- Hydroponics and greenhouses
- Water treatment plants
- Aquaculture systems
- Environmental monitoring
5. What Does EC Sensor Do?
An EC Sensor measures the electrical conductivity of water or solution, which represents the total dissolved salts (TDS) and nutrient strength.
6. How is an EC Sensor different from a TDS meter?
An EC Sensor measures electrical conductivity directly, while a TDS meter converts EC values into estimated total dissolved solids. The EC Sensor provides more accurate and reliable data.






Leave a Reply